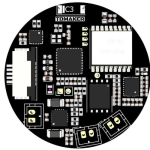
Wi-Fi HaLow is an advanced wireless networking technology based on the IEEE 802.11ah standard, introduced in 2017 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. Operating in the sub-1 GHz frequency band (typically 900 MHz), it offers a longer range and lower power consumption compared to traditional Wi-Fi networks operating at 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz. With a signal reach of up to 1 km (and further under ideal conditions), Wi-Fi HaLow is an ideal solution for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, including sensor networks, wearables, and industrial or agricultural systems, as well as smart city deployments.
Key Features of Wi-Fi HaLow:
- Extended Range: Leveraging lower frequencies, it provides excellent penetration through walls and obstacles, making it suitable for rural or challenging terrains.
- Energy Efficiency: Designed with low-power modes like Target Wake Time (TWT) and Restricted Access Window (RAW), enabling battery-powered devices to operate for months or even years.
- High Device Capacity: A single access point (AP) can connect up to 8,191 devices, surpassing many other IoT protocols.
- Data Speed: Offers a range from 150 kbps to 347 Mbps (depending on bandwidth and conditions), sufficient for video surveillance or large data transfers.
- Security and Compatibility: Utilizes modern Wi-Fi security standards and does not require proprietary hubs or gateways.
Wi-Fi HaLow competes with technologies like Bluetooth, LoRa, Zigbee, and Z-Wave, standing out with its higher speed and broader coverage. It is particularly valuable for applications such as remote monitoring, smart metering, and asset management, where stable connectivity and energy efficiency are critical.
Currently, companies like Morse Micro and AsiaRF are leading the development of Wi-Fi HaLow devices, including modules and dongles supporting long-range connectivity. With its strong growth potential, Wi-Fi HaLow is poised to shape the future of IoT connectivity in 2025 and beyond.
I have included an image below for illustration. Let me know if you’d like me to edit it!
[xaiArtifact artifact_id=”1a2b3c4d-5e6f-7g8h-9i0j-k1l2m3n4o5p6″ title=”Wi-Fi HaLow Post.md” contentType=”text/markdown”]
Wi-Fi HaLow – The Future of IoT Connectivity
Introduction
Wi-Fi HaLow is the IEEE 802.11ah wireless protocol, launched in 2017 by the Wi-Fi Alliance, operating in the sub-1 GHz band (typically 900 MHz). It delivers extended range and lower power usage compared to traditional Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz), ideal for IoT applications.
Technical Advantages
- Range: Up to 1 km with strong obstacle penetration.
- Power Efficiency: Supports TWT and RAW sleep modes for extended battery life.
- Connectivity: Supports 8,191 devices per AP.
- Speed: From 150 kbps to 347 Mbps, suitable for video and large data.
- Security: Integrates modern Wi-Fi standards, no proprietary hub required.
Comparision between some low power technologies:
| Feature | Wi-Fi HaLow | LoRaWAN | Zigbee | Bluetooth LE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Sub-1 GHz | Sub-1 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | Up to 1 km | Up to 15 km | 10-100 m | 10-400 m |
| Data Speed | 150 Kbps – 86.7 Mbps | <50 Kbps | ~250 Kbps | Up to 2 Mbps |
| Power Consumption | High | Very High | High | Very High |
| Native IP Support | Yes | No | No | Partial |
| Number of Devices | Up to 8191 | Thousands | Hundreds | Tens |
Applications
Ideal for sensor networks, wearables, remote monitoring, and smart cities. Competes with Bluetooth, LoRa, and Zigbee with superior speed and range.
Development Status
Morse Micro and AsiaRF, TDMAKER are pioneering Wi-Fi HaLow modules and dongles, with significant growth expected in 2025.

Leave a Reply